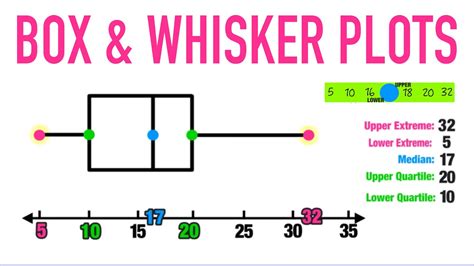
box whisker not normally distributed A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the dataset based on the five-number summary: the minimum, the maximum, the sample median, and the first and third quartiles. • Minimum (Q0 or 0th percentile): the lowest data point in the data set excluding any outliers Vanguard Custom Metals is located at 519 N Hydraulic Ave in Wichita, Kansas 67214. Vanguard Custom Metals can be contacted via phone at 316-910-4826 for pricing, hours and directions. .
0 · upper whisker box plot
1 · difference between box and whiskers
2 · box vs whisker plot
3 · box vs whisker chart
4 · box plot whisker boundary
5 · box and whiskers explained
6 · box and whisker plot example
7 · boundary of lower whisker
As far as I can tell plastic boxes are an inferior box once installed, but plastic are easier/faster to install than metal. For example plastic boxes often have built in nails and romex clamps, while metal boxes lack both.
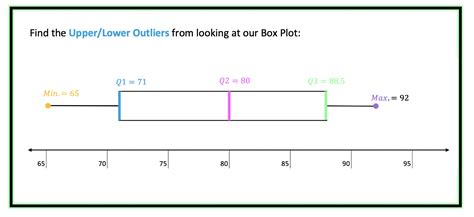
Here's what you find by adding up how many values in each case are below the lower whisker or above the upper whisker: Not bad for the normally distributed data, just 15 .To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and .A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the dataset based on the five-number summary: the minimum, the maximum, the sample median, and the first and third quartiles. • Minimum (Q0 or 0th percentile): the lowest data point in the data set excluding any outliers
Any values that fall beyond these whiskers should be considered outliers; if data is not perfectly normally distributed, the quartiles will vary more in size: In Tableau, the tool for making Box Plots is in the Analytics pane. We can build . Is it the best way to summarize a non-normal distribution? Probably not. Below is a skewed distribution shown as a histogram and a boxplot. You can see the median value of the .The default value for 'Whisker' corresponds to approximately +/–2.7σ and 99.3 percent coverage if the data are normally distributed. The plotted whisker extends to the adjacent value , which is the most extreme data value that is not an outlier.Note that the placement of the box and whiskers is defined in terms of percentiles, not standard deviations, so a box plot does not assume a normal distribution; in fact, it’s another very good .
Box and whisker plots are a powerful tool for visually understanding the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to see the spread of the data, identify outliers, and compare .
upper whisker box plot
The graph represents a normal distribution in a data set, with the σ symbol representing a standard distribution. The box plot will rarely look this perfect, however it will still show how our . The box plot shape will show if a statistical data set is normally distributed or skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box, and the whiskers are about the same on both sides of the box, then the distribution is symmetric. Here's what you find by adding up how many values in each case are below the lower whisker or above the upper whisker: Not bad for the normally distributed data, just 15 instead of 10: sum(nvals < boxn $stats[1,1] | nvals > boxn$ stats[5,1]) # [1] 15 But for the others (lognormal, 2-df t and 1-df t in order):To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.
Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).
difference between box and whiskers
If I plot some data in function of a categorical variable in R, I get the standard boxplot. However, the boxplot displays non-parametric statistics (quantiles) that don't seem appropriate for normally distributed data. What is the equivalent of the boxplot for normally distributed data (ideally, something based on confidence intervals?) ?Any values that fall beyond these whiskers should be considered outliers; if data is not perfectly normally distributed, the quartiles will vary more in size: In Tableau, the tool for making Box Plots is in the Analytics pane. We can build one out using Superstore data.
A simpler formulation is this: no whisker will be visible if the lower quartile is equal to the minimum, or if the upper quartile is equal to the maximum. (There are other cases in which no whisker is visible.)
Is it the best way to summarize a non-normal distribution? Probably not. Below is a skewed distribution shown as a histogram and a boxplot. You can see the median value of the boxplot is accurate and the quartile markers (the edges of the 'box') show the skew. The outliers also indicate a skew.The default value for 'Whisker' corresponds to approximately +/–2.7σ and 99.3 percent coverage if the data are normally distributed. The plotted whisker extends to the adjacent value , which is the most extreme data value that is not an outlier.
Note that the placement of the box and whiskers is defined in terms of percentiles, not standard deviations, so a box plot does not assume a normal distribution; in fact, it’s another very good tool for deciding whether your data is normally distributed. The box plot shape will show if a statistical data set is normally distributed or skewed. When the median is in the middle of the box, and the whiskers are about the same on both sides of the box, then the distribution is symmetric. Here's what you find by adding up how many values in each case are below the lower whisker or above the upper whisker: Not bad for the normally distributed data, just 15 instead of 10: sum(nvals < boxn $stats[1,1] | nvals > boxn$ stats[5,1]) # [1] 15 But for the others (lognormal, 2-df t and 1-df t in order):
steel boxes manufacturers mysore
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.Box plots are non-parametric: they display variation in samples of a statistical population without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution [3] (though Tukey's boxplot assumes symmetry for the whiskers and normality for their length).
If I plot some data in function of a categorical variable in R, I get the standard boxplot. However, the boxplot displays non-parametric statistics (quantiles) that don't seem appropriate for normally distributed data. What is the equivalent of the boxplot for normally distributed data (ideally, something based on confidence intervals?) ?Any values that fall beyond these whiskers should be considered outliers; if data is not perfectly normally distributed, the quartiles will vary more in size: In Tableau, the tool for making Box Plots is in the Analytics pane. We can build one out using Superstore data. A simpler formulation is this: no whisker will be visible if the lower quartile is equal to the minimum, or if the upper quartile is equal to the maximum. (There are other cases in which no whisker is visible.)
Is it the best way to summarize a non-normal distribution? Probably not. Below is a skewed distribution shown as a histogram and a boxplot. You can see the median value of the boxplot is accurate and the quartile markers (the edges of the 'box') show the skew. The outliers also indicate a skew.The default value for 'Whisker' corresponds to approximately +/–2.7σ and 99.3 percent coverage if the data are normally distributed. The plotted whisker extends to the adjacent value , which is the most extreme data value that is not an outlier.
steel box spring reviews
box vs whisker plot
A deteriorating septic tank shows white fiber reinforcements becoming visible. It may show up as white crumbling concrete around an outlet or as rusty streaks on the side of a tank, but it comes down to the same problem septic professionals have been seeing for years – a deteriorating septic tank.
box whisker not normally distributed|upper whisker box plot